1.DFS—深度优先搜索 排列数字 给定一个整数 n,将数字 1∼n 排成一排,将会有很多种排列方法。
现在,请你按照字典序将所有的排列方法输出。
输入格式 共一行,包含一个整数 n。
输出格式
数据范围
输入样例:
输出样例:
1 2 3 4 5 6 1 2 3 1 3 2 2 1 3 2 3 1 3 1 2 3 2 1
「完整代码:」
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;const int N = 10 ;int n;int path[N];bool st[N];void dfs (int x) if (x == n) { for (int i = 0 ; i < n;i++) { cout << path[i] + 1 << " " ; } cout << endl; return ; } for (int i = 0 ; i < n;i++) { if (!st[i]) { path[x] = i; st[i] = true ; dfs (x+1 ); st[i] = false ; } } } int main () cin >> n; dfs (0 ); return 0 ; }
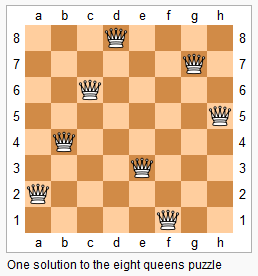
n皇后问题 n−皇后问题是指将 n个皇后放在 n×n 的国际象棋棋盘上,使得皇后不能相互攻击到,即任意两个皇后都不能处于同一行、同一列或同一斜线上。
现在给定整数 n,请你输出所有的满足条件的棋子摆法。
输入格式
输出格式
其中 . 表示某一个位置的方格状态为空,Q 表示某一个位置的方格上摆着皇后。
每个方案输出完成后,输出一个空行。
注意:行末不能有多余空格。
输出方案的顺序任意,只要不重复且没有遗漏即可。
数据范围
输出样例: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 .Q.. ...Q Q... ..Q. ..Q. Q... ...Q .Q..
「解决思路:」
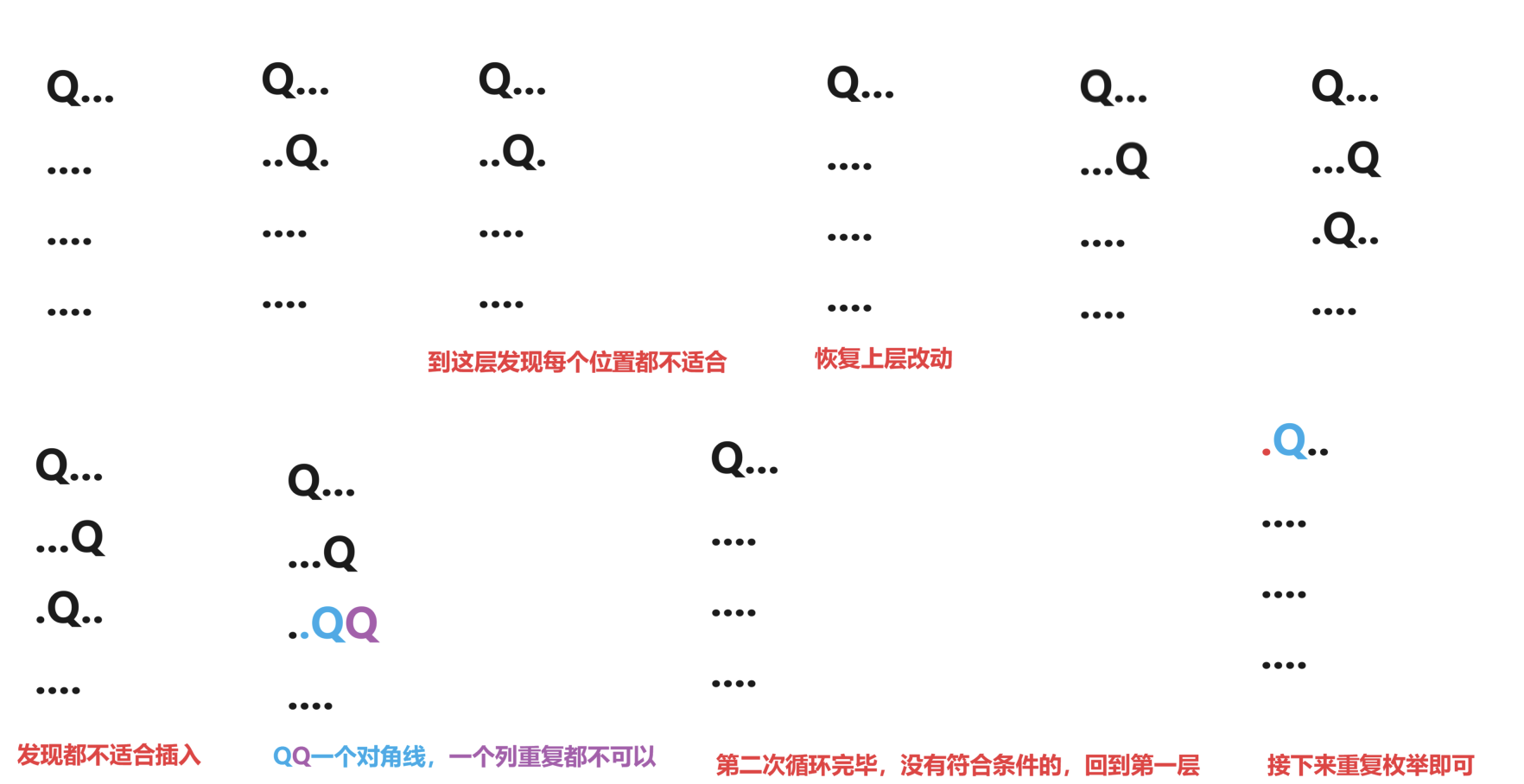
我们可以利用深搜,一行一行来解决,每一行里面的每一列都可以试着枚举一下设置为Q,然后此点的两条对角线设置为true已使用,此列设置为已使用,之后在遍历下一行。
如果遇到某一行没有符合条件的,即这一层for循环调用完毕后,没有触发if函数
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 for (int i = 0 ; i < n;i++) { if (!col[i] and !dg[u+i] and !udg[u-i+n]) { arr[u][i] = 'Q' ; col[i] = true ; dg[u+i] = true ; udg[u - i +n] = true ; dfs (u+1 ); col[i] = false ; dg[u+i] = false ; udg[u - i +n] = false ; arr[u][i] = '.' ; } }
然后本层dfs运行结束后,回溯到上层调用的地方,说明此路不通,恢复上一层改动
1 2 3 4 5 dfs (u+1 ); col[i] = false ; dg[u+i] = false ; udg[u - i +n] = false ; arr[u][i] = '.' ;
然后继续for循环判断下一个位置是否可以改为‘Q’,继续判断,直到找出结果。
「图解:」
「完整代码:」
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;const int N = 20 ;char g[N][N];bool col[N], dg[N], udg[N];int n;void dfs (int u) if (u == n) { for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) { cout << g[i] << endl; } cout << endl; return ; } for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) { if (!col[i] and !dg[u + i] and !udg[u - i + n]) { g[u][i] = 'Q' ; col[i] = dg[u + i] = udg[u - i + n] = true ; dfs (u + 1 ); col[i] = dg[u + i] = udg[u - i + n] = false ; g[u][i] = '.' ; } } } int main () cin >> n; for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) { for (int j = 0 ; j < n; j++) { g[i][j] = '.' ; } } dfs (0 ); return 0 ; }
2.BFS—广度优先搜索 迷宫问题 给定一个 n×m 的二维整数数组,用来表示一个迷宫,数组中只包含 0 或 1,其中 0 表示可以走的路,1、 表示不可通过的墙壁。
最初,有一个人位于左上角 (1,1)处,已知该人每次可以向上、下、左、右任意一个方向移动一个位置。
请问,该人从左上角移动至右下角 (n,m)处,至少需要移动多少次。
数据保证 (1,1)处和 (n,m) 处的数字为 0,且一定至少存在一条通路。
输入格式第一行包含两个整数 n和 m。
接下来 n 行,每行包含 m 个整数(0 或 1 ),表示完整的二维数组迷宫。
输出格式
数据范围
1 2 3 4 5 6 5 5 0 1 0 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 1 0
输出样例:
「解题思路:」
此题从起点开始,每次向四周(上下左右)扩散,在没个点的位置上记录起点到这个点的距离,之后遍历完成后,输出右下角的距离值,此题完成。
「变量介绍:」
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 using ll = long long ;using PII = pair<int , int >; const int N = 105 ; int n, m; int g[N][N]; int d[N][N]; queue<PII> q;
「函数详解:」
此题核心!!!!!!!!!!!
对于此题的路径就是按图中所示,如果旁边的点不为1可以走,那么则会把四周的依次填入队列中,并且把距离数组d中相应的该点加上前面路径的距离。
1 2 3 4 5 if (x >= 0 and y >= 0 and x < n and y < m and g[x][y] == 0 and d[x][y] == -1 ) { d[x][y] = d[t.first][t.second] + 1 ; q.push ({x,y}); }
对于附近的点,则使用偏移向量进行更新,每次循环四次,加上偏移量,则对应上下左右。
1 2 3 4 5 6 int dx[4 ] = {-1 , 0 , 1 , 0 }; int dy[4 ] = {0 , 1 , 0 , -1 }; int x = t.first + dx[i];int y = t.second + dy[i];
「路径变化:」
「队列变化:」
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 int dfs () q.push ({0 , 0 }); memset (d, -1 , sizeof d); d[0 ][0 ] = 0 ; int dx[4 ] = {-1 , 0 , 1 , 0 }; int dy[4 ] = {0 , 1 , 0 , -1 }; while (!q.empty ()) { auto t = q.front (); q.pop (); for (int i = 0 ; i < 4 ;i++) { int x = t.first + dx[i]; int y = t.second + dy[i]; if (x >= 0 and y >= 0 and x < n and y < m and g[x][y] == 0 and d[x][y] == -1 ) { d[x][y] = d[t.first][t.second] + 1 ; q.push ({x,y}); } } } return d[n-1 ][m-1 ]; }
「完整代码:」
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;using ll = long long ;using PII = pair<int , int >;const int N = 105 ;int n, m;int g[N][N]; int d[N][N]; queue<PII> q; int dfs () q.push ({0 , 0 }); memset (d, -1 , sizeof d); d[0 ][0 ] = 0 ; int dx[4 ] = {-1 , 0 , 1 , 0 }; int dy[4 ] = {0 , 1 , 0 , -1 }; while (!q.empty ()) { auto t = q.front (); q.pop (); for (int i = 0 ; i < 4 ;i++) { int x = t.first + dx[i]; int y = t.second + dy[i]; if (x >= 0 and y >= 0 and x < n and y < m and g[x][y] == 0 and d[x][y] == -1 ) { d[x][y] = d[t.first][t.second] + 1 ; q.push ({x,y}); } } } return d[n-1 ][m-1 ]; } int main () cin >> n >> m; for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) for (int j = 0 ; j < m; j++) cin >> g[i][j]; cout << dfs () << endl; return 0 ; }
八段码 在一个 3×33×3 的网格中,1∼81∼8 这 88 个数字和一个 x 恰好不重不漏地分布在这 3×33×3 的网格中。
例如:
在游戏过程中,可以把 x 与其上、下、左、右四个方向之一的数字交换(如果存在)。
我们的目的是通过交换,使得网格变为如下排列(称为正确排列):
例如,示例中图形就可以通过让 x 先后与右、下、右三个方向的数字交换成功得到正确排列。
交换过程如下:
1 2 3 1 2 3 1 2 3 1 2 3 1 2 3 x 4 6 4 x 6 4 5 6 4 5 6 7 5 8 7 5 8 7 x 8 7 8 x
现在,给你一个初始网格,请你求出得到正确排列至少需要进行多少次交换。
输入格式 输入占一行,将 3×33×3 的初始网格描绘出来。
例如,如果初始网格如下所示:
则输入为:1 2 3 x 4 6 7 5 8
输出格式 输出占一行,包含一个整数,表示最少交换次数。
如果不存在解决方案,则输出 −1−1。
输入样例: 输出样例 「解题思路:」
典型的求最短路问题,可以使用BFS
可以 利用一维数组转为二维数组的方式巧妙解决本题
先求出 x 原本的一维数组坐标,然后利用以下代码进行转为二维坐标
1 2 3 4 5 6 int index_x = front_str.find ('x' ); int double_x = index_x / 3 ; int double_y = index_x % 3 ;
之后在 x 的二维坐标基础上上下左右移动,求出对应的二维坐标,再将四个上下左右进行转为一维坐标,交换x与其上下左右的值,如果之前没出现过交换后的字符串的状态,进行次数加一。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 for (int i = 0 ; i < 4 ; i++) { int two_a = double_x + dx[i]; int two_b = double_y + dy[i]; if (two_a < 3 and two_a >= 0 and two_b < 3 and two_b >= 0 ) { int one_ab = two_a * 3 + two_b; swap (temp_str[index_x], temp_str[one_ab]); if (!d.count (temp_str)) { q.push (temp_str); d[temp_str] = d[front_str] + 1 ; } swap (temp_str[index_x], temp_str[one_ab]); } }
「变量介绍:」
1 2 3 4 const string end_str = "12345678x" ; unordered_map<string, int > d; queue<string> q;
「完整代码:」
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;const string end_str = "12345678x" ; unordered_map<string, int > d; queue<string> q; int bfs (string start_str) d[start_str] = 0 ; int dx[4 ] = {-1 , 1 , 0 , 0 }, dy[4 ] = {0 , 0 , 1 , -1 }; q.push (start_str); while (!q.empty ()) { string front_str = q.front (); string temp_str = front_str; if (temp_str == end_str) return d[temp_str]; q.pop (); int index_x = front_str.find ('x' ); int double_x = index_x / 3 ; int double_y = index_x % 3 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < 4 ; i++) { int two_a = double_x + dx[i]; int two_b = double_y + dy[i]; if (two_a < 3 and two_a >= 0 and two_b < 3 and two_b >= 0 ) { int one_ab = two_a * 3 + two_b; swap (temp_str[index_x], temp_str[one_ab]); if (!d.count (temp_str)) { q.push (temp_str); d[temp_str] = d[front_str] + 1 ; } swap (temp_str[index_x], temp_str[one_ab]); } } } return -1 ; } int main () string s1; for (int i = 0 ; i < 9 ; i++) { char c1; cin >> c1; s1 += c1; } int res = bfs (s1); cout << res << endl; return 0 ; }